Taking care of your health is essential, especially when it comes to your heart. Not many people worry about their heart health until it’s too late. They may even have rheumatic heart disease without knowing it.
So what should you look out for? Here are ten signs and symptoms that you may have rheumatic heart disease.
What Is Rheumatic Heart Disease?
This is a heart condition in which the valves have become permanently damaged through rheumatic fever. The damage can occur shortly after a strep infection that has been left untreated or undertreated. Rheumatic fever causes connective tissues to become inflamed, leading to scar tissue being formed. Because this affects the heart valves, they’ll become more narrow or start leaking, which affects the normal functioning of the heart.
What Are the Ten Common Symptoms of Rheumatic Heart Disease?
Usually, rheumatic fever is diagnosed first before a test is done for rheumatic heart disease. The most common symptoms of rheumatic fever include:
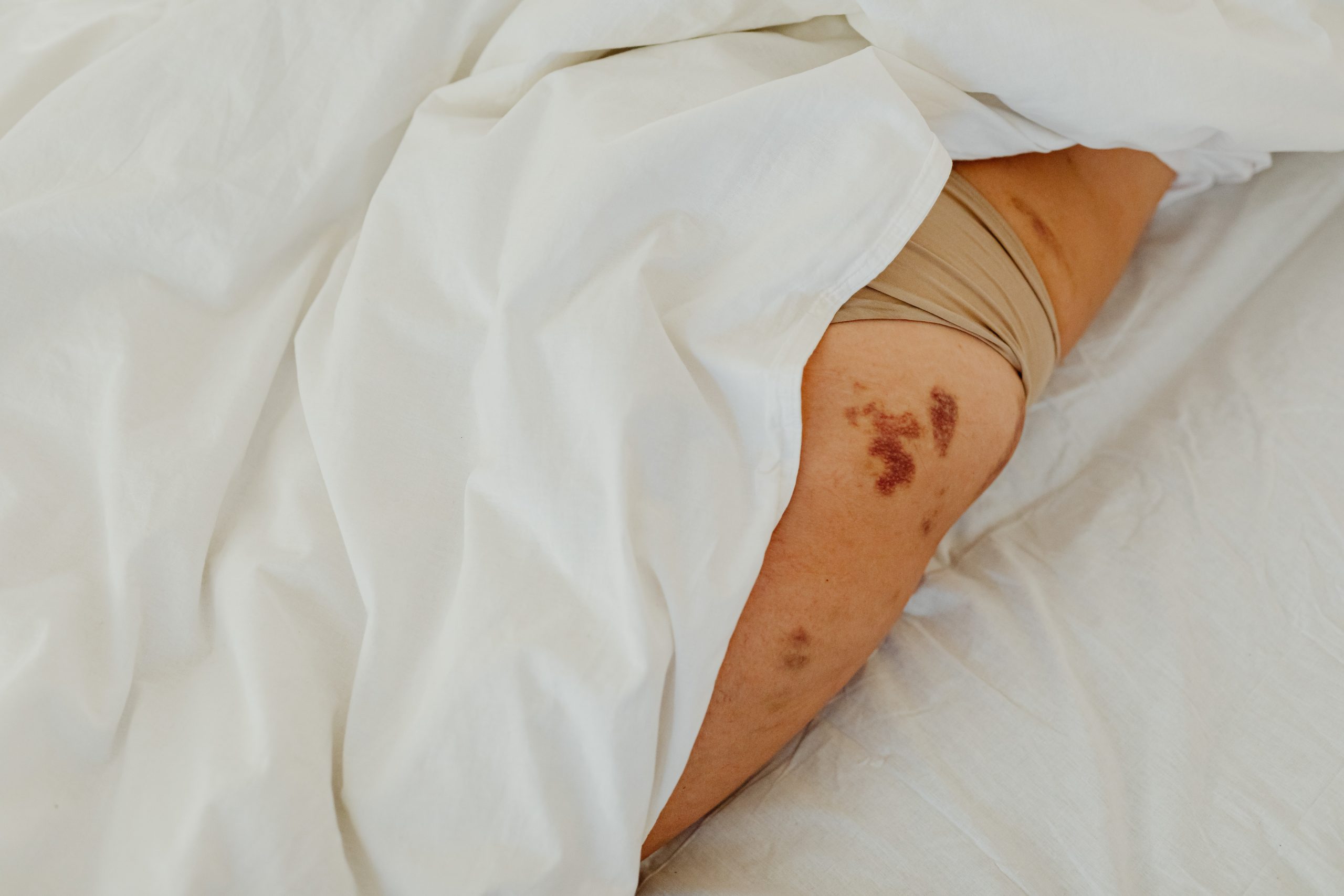
- swollen and painful joints, including the knees and ankles
- lumps appearing under the skin
- fever
- weakness
- red, raised rash across the back, chest, and abdomen
- chest discomfort and shortness of breath
- uncontrolled movement of facial muscles, legs, and arms
Once a rheumatic fever subsides, the symptoms of rheumatic heart disease may present themselves. These include:
- swelling
- shortness of breath (especially when lying down)
- chest pain
Being aware of these symptoms will help you seek medical attention sooner rather than later.
How is Rheumatic Heart Disease Diagnosed?
There are several methods that can be used to diagnose the disease. Firstly, a simple physical exam can reveal the first sign. By listening to the chest, your doctor may hear a heart murmur, which is caused by blood leaking around the damaged valves. Your doctor may also hear a rub, which is the inflamed heart tissues rubbing against each other.
Other methods of diagnosing rheumatic heart disease include blood tests, chest X-ray, echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, and cardiac MRI.
How Is Rheumatic Heart Disease Treated?
Treatment involves taking care of the valves of the heart. In very severe cases, surgery to repair or replace a damaged heart valve is possible. Otherwise, the best way to prevent rheumatic heart disease is to prevent the initial rheumatic fever. Antibiotics can be used to treat strep throat and prevent rheumatic fever from occurring. Anti-inflammatory drugs can also be used to reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of the heart becoming damaged. Someone who has had rheumatic fever may have to take antibiotics for the rest of their lives in order to prevent other infections from occurring in the future.
Rheumatic fever should be taken very seriously in order to prevent rheumatic heart disease from occurring in the future. Although there is no vaccine to prevent the infection, you should always take precautionary steps to prevent the infection from happening in the first place. Wash hands on a regular basis, cover your mouth when you sneeze or cough, and don’t share personal items that can increase the spread of infection, such as drinking glasses or toothbrushes.