What is Lumbago?
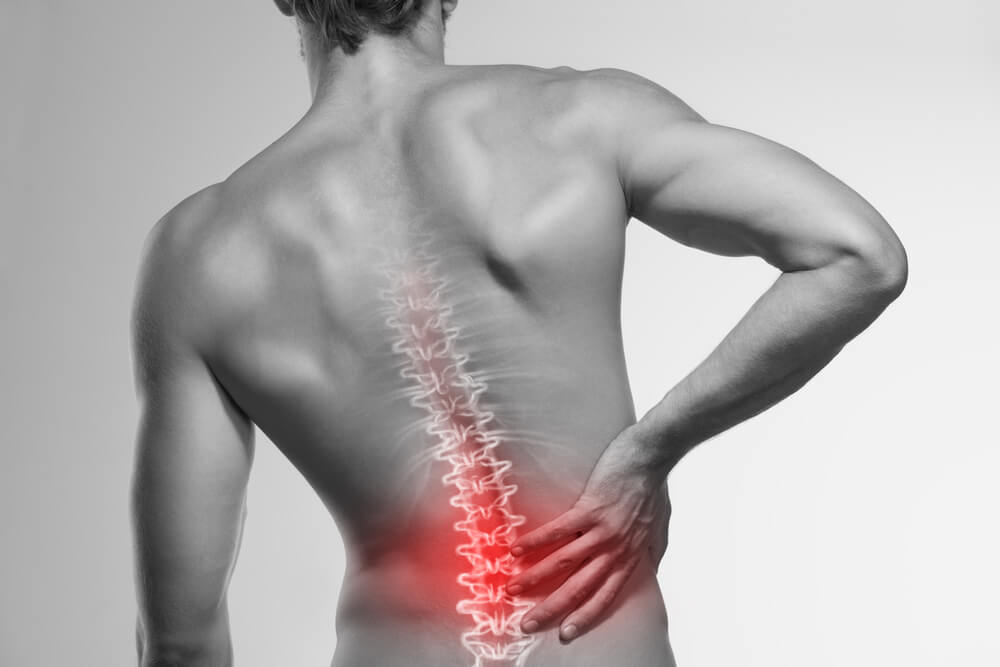
Lumbago is an older, non-medical term for back pain or pain in the lower back. Lumbago can make the low back, buttocks, and legs feel on fire. Lumbago rarely causes severe symptoms that need to be treated right away by a doctor. But it is good to be aware of the signs like Loss of control over your bladder or bowels, tingling, or weakness in your legs.
What Are The Causes Of Lumbago?
Lumbago or lower back pain can be caused by many injuries, conditions, and diseases. Among them are:
Injuries like sprains and strains
An important common cause of back discomfort is a strain or sprain. You can hurt your muscles lifting something too heavy or not safe, tendons or ligaments. Some people break their backs by coughing, sneezing, turning, or bending over.
Fractures
Spinal bones, like a vehicle collision or a tumble, may shatter in an accident.
Disks’ problems
They are pads for the vertebrae (small spinal bones). Disks can push on nerves if they move out of place in the spine. Also, they can tear (herniated disk). As disks age, they can flatten and protect less (degenerative disk disease).
Issues with the Spine
Spinal stenosis generally occurs when the spinal column is too small to accommodate the spinal cord’s diameter.
When something pinches the spinal cord, it can cause much pain in the lower back and along the sciatic nerve. Scoliosis, a curved spine, can cause pain, stiffness, and trouble moving.
Osteoarthritis
Lower back discomfort may be caused by osteoarthritis, the most prevalent type of arthritis. Ankylosing spondylitis makes the spine stiff and inflamed and hurts the lower back.
Spine Tumors
Back pain can be caused by some diseases, such as spine tumors, infections, and some types of cancer. Other things can also cause back pain. Some of these are kidney stones and an aortic aneurysm in the abdomen.
Spondylolisthesis
It is when the spine’s vertebrae move out of place. Spondylolisthesis causes pain in the lower back and the legs.
Lumbago displays these symptoms.
If you’re experiencing pain, it might be anything from mild to excruciatingly severe or shooting. Because of the discomfort, moving or standing up straight may not be easy. The term “acute” refers to pain that occurs suddenly. It may occur due to strenuous physical activity or heavy lifting. Pain that persists for longer than three months is referred to as chronic.
Signs of Lumbago That Need Immediate Care
You should see a doctor if you fall or hurt yourself and your back hurts. The same is true if you have back pain and trouble controlling your bowels or bladder, weak legs, a fever, or pain when coughing or peeing.
Lumbago Signs and Symptoms
The back of the thigh, buttocks, and thighs may also be affected by Lumbago. Back pain, called Lumbago, can be made worse by movement. Bending forward, backward, or to the side can hurt, making it hard to do things. Spinal muscle spasms cause back pain and stiffness.
Lumbago’s most common symptoms include:
- Pain in my lower back
- Muscle Spasm
- Burning
- Stiffness
Different ways to treat Lumbago
Lumbago can be treated in many different ways, depending on the patient’s age, weight, level of activity, and much more. Here are some ways to treat it:
● Anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain temporarily, hot or cold packs, exercise, and gentle stretches
● Try to Avoid heavy lifting through yoga, acupuncture, chiropractic, spinal manipulation, surgery, and physical therapy.
● Quit Smoking.
How to Diagnose Lumbago?
Your doctor or nurse will ask you about your symptoms, and they’ll examine you. They may order imaging tests to check for fractures or other injuries. The doctor may see all of your vertebrae, discs, and muscles clearly in these tests. Your physician may prescribe an X-ray of the spine.
Some things doctors might also ask for:
● Spine X-ray.
● MRI usually uses radio waves and a magnet to produce images of soft tissues such as bones, muscles, and tendons.
● CT scan to make 3D pictures of bones and soft tissues.
● Electromyography (EMG) tests nerves and muscles and looks for nerve damage (neuropathy), making your legs tingly or numb.
Urine or Blood tests usually may be ordered by your doctor, depending on the cause of your discomfort. Blood testing may reveal genetic markers for specific back pain issues (such as ankylosing spondylitis). Kidney stones, which hurt in the side, are checked for in urine tests (the sides of the low back).
Can I stop having pain in my Lumbago?
You can’t stop lower back pain from a disease or a problem with how the spine is built. But you may avoid injury to your back if you take precautions. Maintain a healthy weight. The spine and disks are placed under more strain when one is overweight.
Keep your weight at a healthy level.
Having extra weight puts pressure on the spine and discs.
Make sure you’re working on your abs. Pilates and other exercises strengthen the core muscles that support the spine.
How to lift right:
- Avoid getting hurt by lifting with your legs, not your back.
- Keep heavy items close to your body to avoid back pain.
- When lifting, try not to twist or turn your body.
What are people who suffer from lower back pain likely to do in the meantime?
The pain can influence the outcome of a situation. People who strain or sprain their backs recover and do not suffer long-term health consequences. Many individuals will have another incident within a year.
Some people have back pain that lasts for weeks and doesn’t disappear. Conditions that worsen over time, like arthritis and osteoporosis, can worsen older people’s symptoms. People having several injuries and illnesses can get rid of pain with surgery and other treatments.